Random Variables in Statistics
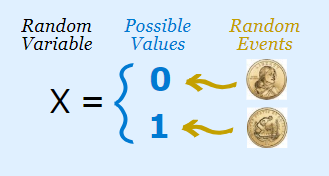
A Random Variable is any rule that maps (links) a number with each outcome in sample space S. Mathematically, random variable is a function with Sample Space as the domain. It’s range is the set of Real Numbers.
Random Variables in Statistics Read More »